Determination of earthquake magnitudes using duration of
high-frequency energy radiation and maximum displacement amplitudes: application
to the November 7, offshore Guatemala earthquake
Tatsuhiko Hara
International
Building Research Institute
We developed a method to determine
earthquake magnitudes using the following formula (Hara, 2007a, b):
![]()
where M is an earthquake magnitude, ![]() is the maximum
displacement during high-frequency energy radiation from the arrival time of a
P-wave,
is the maximum
displacement during high-frequency energy radiation from the arrival time of a
P-wave, ![]() is the epicentral distance,
is the epicentral distance, ![]() is duration of
high-frequency energy radiation. The duration of high-frequency energy
radiation can be estimated by band-pass filtering of first arriving P-waves (e.g.,
Hara, 2007a).
is duration of
high-frequency energy radiation. The duration of high-frequency energy
radiation can be estimated by band-pass filtering of first arriving P-waves (e.g.,
Hara, 2007a). ![]() are 0.79, 0.83, 0.69,
and 6.47, respectively (the units of
are 0.79, 0.83, 0.69,
and 6.47, respectively (the units of ![]() were m, km, and s,
respectively).
were m, km, and s,
respectively).
We applied this method to the November 7, offshore Guatemala earthquake (the
origin time: 16:35:50 UTC; the location 14.083N, 91.916W after USGS). Figure
1 shows an example of measurements of high-frequency energy radiation. The estimated duration is 18.3 sec. The
estimated magnitude using the above formula is 7.29, which is
consistent with Mw 7.3 from the Global CMT solution and Mww 7.4 from USGS WPhase
Moment Tensor Solution.
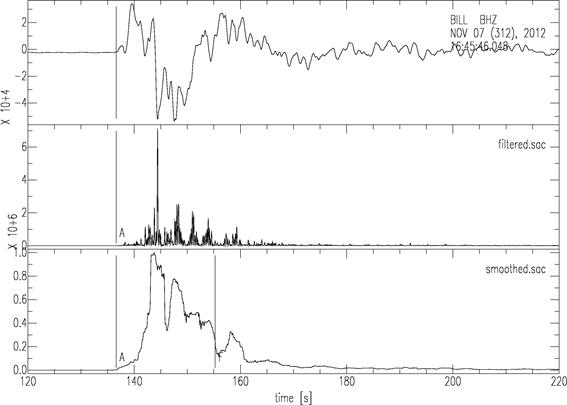
Fig. 1. An example of measurements of high
frequency energy radiation. The upper, middle and lower traces are an observed
seismogram, the squares of the band-pass (2-4 Hz) filtered seismogram, and its
smoothed time series (normalized by the maximum value), respectively. gAh and
gFh in the lower trace denote the arrival of P-wave and estimated end of high
frequency energy radiation, respectively.
References
Hara, T., Measurement of duration of
high-frequency energy radiation and its application to determination of
magnitudes of large shallow earthquakes, Earth Planets Space, 59,
227–231, 2007a.
Hara, T., Magnitude
determination using duration of high frequency energy radiation and
displacement amplitude: application to tsunami earthquakes, Earth Planets Space, 59, 561–565, 2007b.
Last Updated: 2012/11/08