Regression analysis was performed using observed tsunami height at offshore and coastal tidal station pairs, which were within 20 km each other, for the 2010 Chile earthquake tsunami. We used 26 sets initial and 33 sets maximum tsunami height data obtained from the Real-Time Kinematic Global Positioning System (RTK-GPS) buoys, wave stations and coastal tidal stations throughout Japan. We obtained the formulas for initial and maximum tsunami height as
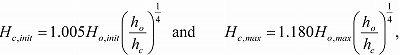
where Ho,init and Ho,max are the initial and maximum tsunami height observed at an offshore station, Hc,init and Hc,max are the initial and maximum tsunami height observed at a coastal tidal station, ho and hc are the water depth at an offshore and coastal tidal station from the mean sea level. In the previous study, similar proportional parameters have been derived. Tsunami simulation of the 1896 Sanriku earthquake tsunami was performed as a case study of application of these equations to real time tsunami forecast and tsunami database. Then, we conclude that the former formula is reliable and valuable enough to be applied in real time tsunami forecast using detected initial tsunami wave at offshore RTK-GPS buoy, because of the potentially increased leading time to issue tsunami warning. In addition, preparing maximum tsunami height data by applying the latter formula and using synthetic tsunami waveforms at forecast points or RTK-GPS buoys should improve the accuracy of tsunami database.